Deploy WordPlate Wordpress Sites
WordPlate is a WordPress boiler plate that is a great for development-minded WordPress users.
With WordPlate, you can update WordPress locally on your device, and then deploy the finished product out using the deployment workflow deployment method in Cleavr.
Another benefit of WordPlate is that you can benefit from some of the enhancements and more modern development methods that they've introduced. Such as, you can
make use of a .env file to maintain environment variables, such as database connections.
Step 1: Install WordPlate
The first step is to install WordPlate on your local device.
Follow the WordPlate instructions on their README file to get going.
Once installed, build your WordPress site on your local environment and continue on to the following instructions when ready to deploy.
Step 2: Commit Your Code To A Version Control Repository
Add your code to GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab.
Step 3: Add Server And Site
In Cleavr, provision a new server.
Once the server has completed setup, add a new PHP site to the server and enter public for the Web Directory.
Also, select the advance option to also create a database during site creation. Remember the database details as you'll need to add them later to the environment section.
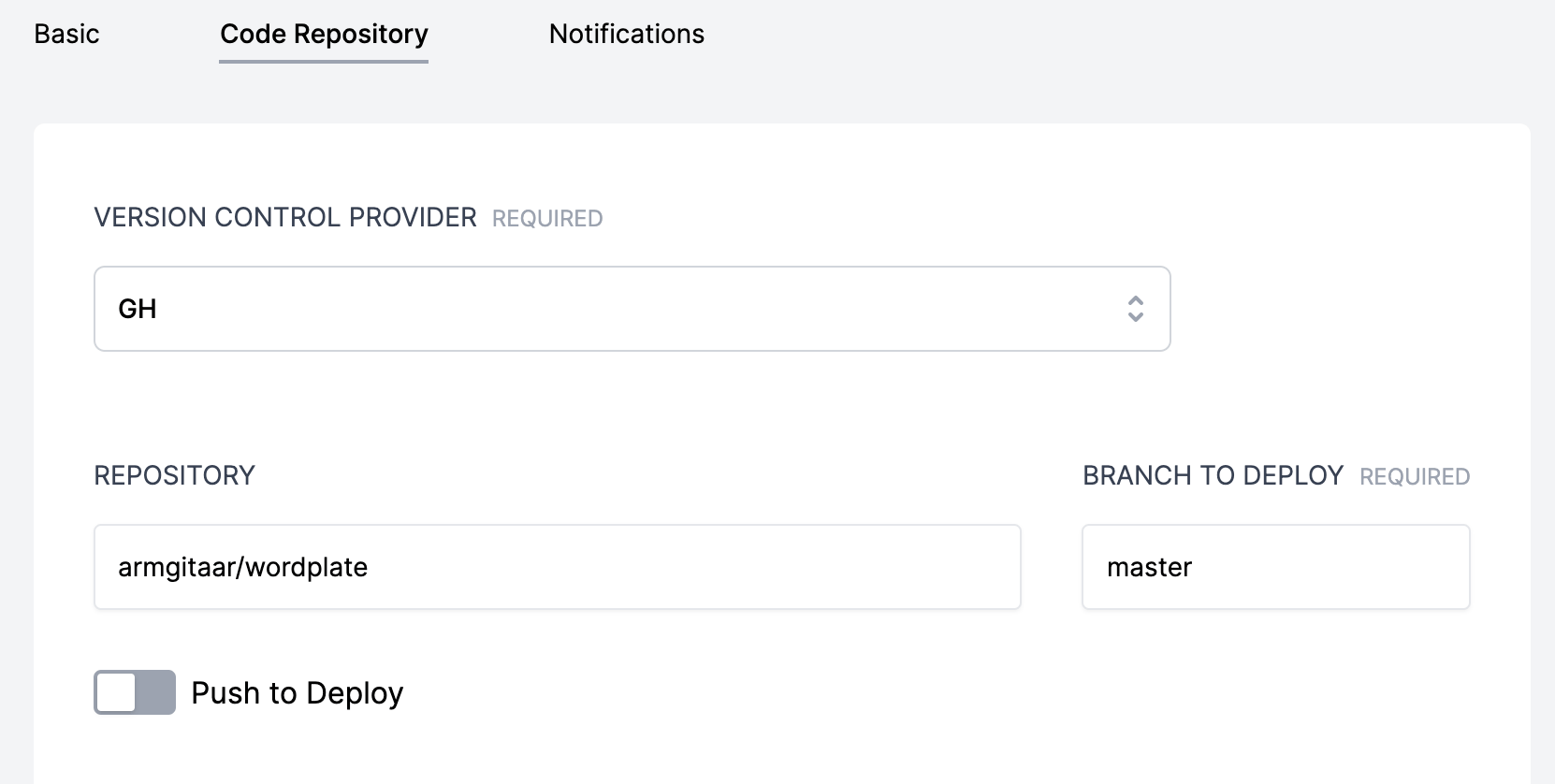
Step 4: Configure Deployment Workflow Code Repository
Navigate to the deployment workflow section. You'll notice that a new deployment workflow has been added after adding the site. This is the master deployment workflow that we'll configure to deploy the WordPlate site to the server.
Click into the deployment workflow, then go to Settings > Code Repository and select the VC Provider for where your code is and then enter the Repository and Branch To Deploy info.
Step 5: Add Environment Variables
On the Environment tab, add in the .env variables.
They should look something like the following.
WP_ENV=production
WP_DEBUG=false
WP_THEME=wordplate
WP_PREFIX=wp_
DB_HOST=<db public ip>
DB_NAME=<database name>
DB_USER=<database user>
DB_PASSWORD=<database password>
# https://wordplate.github.io/salt/
AUTH_KEY=ded006be9d2b242c4df043608b399f5537c8da79916a21ae8c23a2e4156e3799
SECURE_AUTH_KEY=b1e61db85cfafa226f70abba8cfcac70c1bbcf07cc7c82f7d718c1eb4bf5ae2b
LOGGED_IN_KEY=fdc6684804ac7b72ec485c7588dd78f9989950a935ae2a35a6d750285314f78f
NONCE_KEY=676ae2e9befe1b22822bd973bcf7c1c3f4748fe6d272ea2667146832484bdff2
AUTH_SALT=54f005e47227616aa6daf26a2fd4db97b71f6a570022ed7383383bd7d225eb42
SECURE_AUTH_SALT=07f46a835f5caa39007de9c65e1f3a2c8fdd81c8164a2be61bb5312c68305180
LOGGED_IN_SALT=e5035645134537babf04473773108a056513c51c99281c7da80752633a63d409
NONCE_SALT=c99c4ecae2a722fa70fccb918cc5757327bc9e5897ed42c7eb4852bbd37a5bd3
Click sync to save variables.
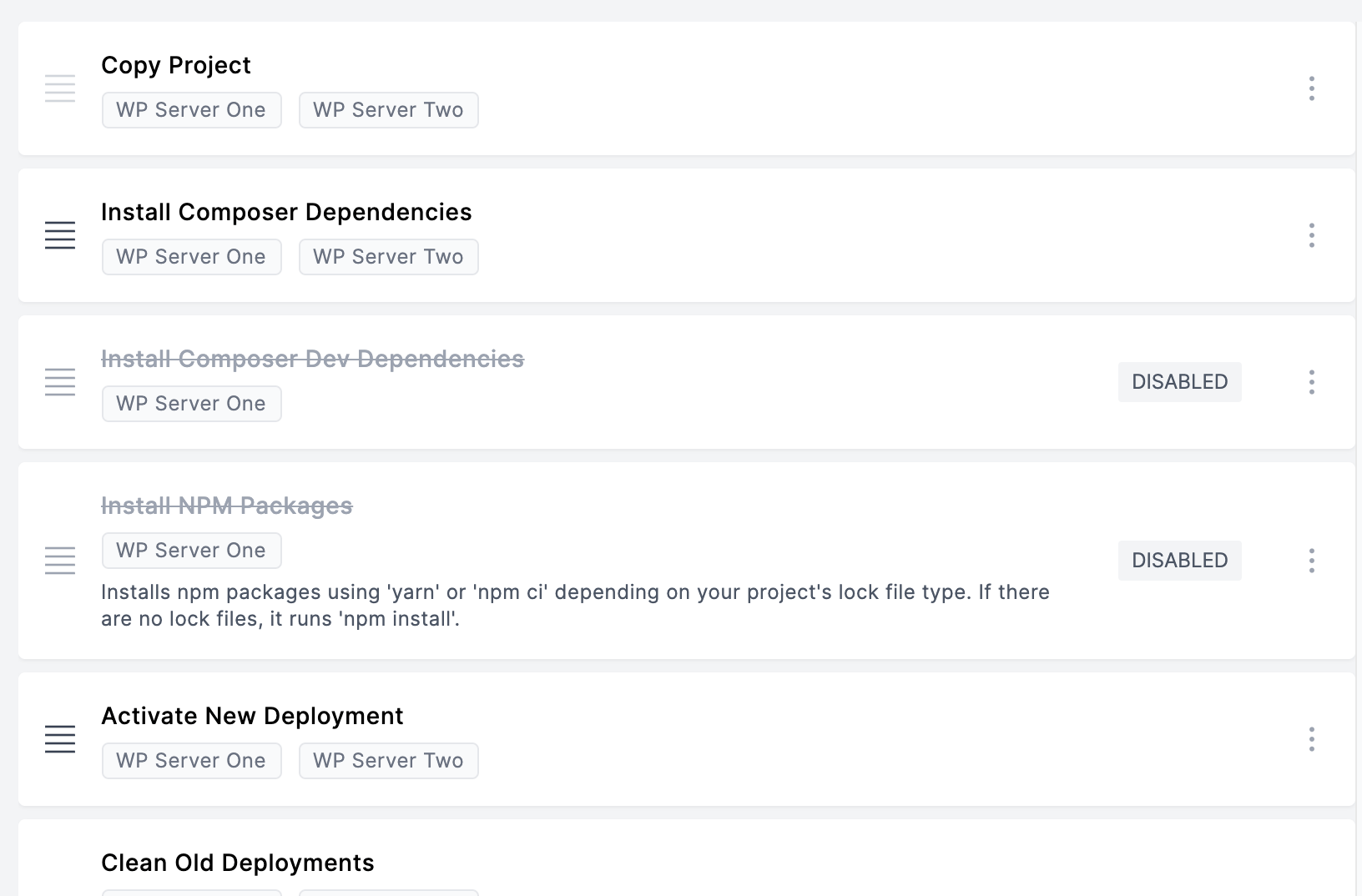
Step 6: Verify deployment hooks
Go to the Deployment Hooks section and enable Install Composer Dependencies hook.
Step 7: Deploy! 🚀
You can now deploy your app!
